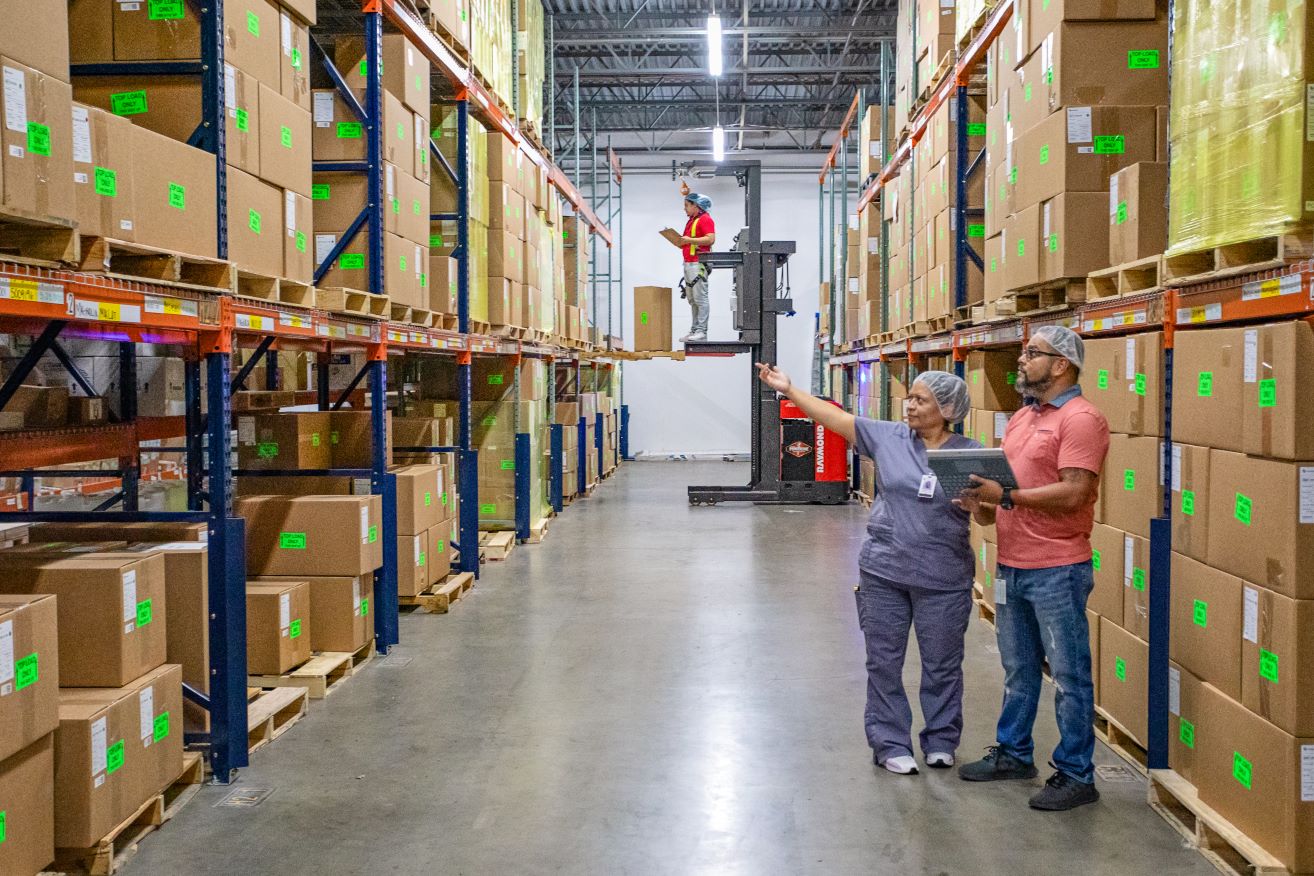
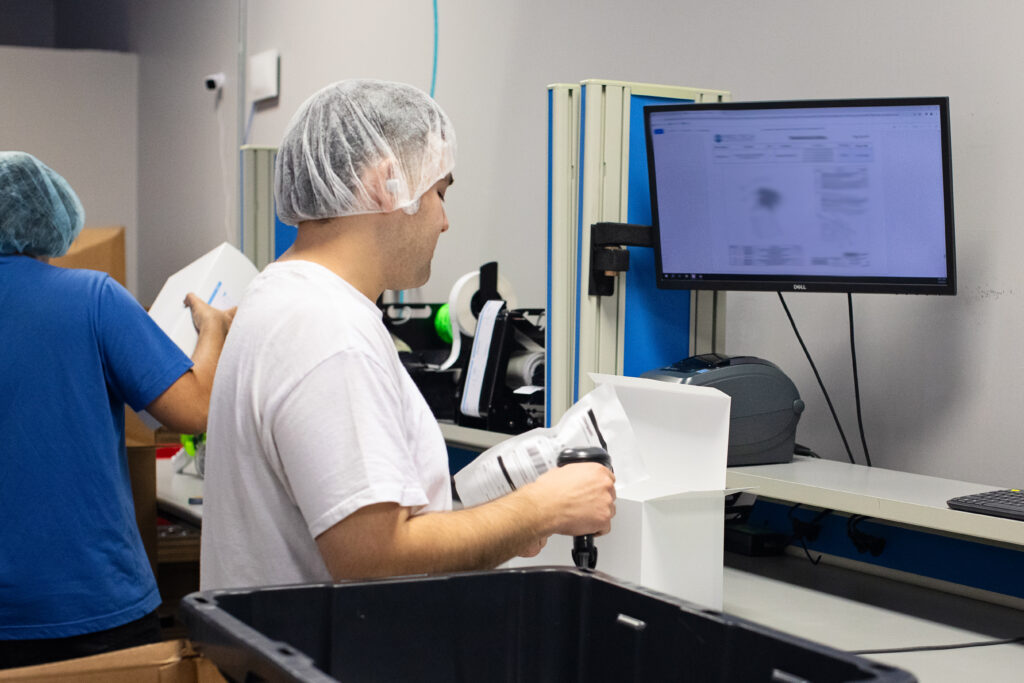
The role of packaging in the medical device supply chain goes far beyond protection—it shapes how products are transported, stored, and presented to end-users. For medical device manufacturers, effective packaging design is key to maintaining quality, reducing risks, and meeting regulatory demands. It is a vital component of supply chain management that affects every stage, from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished products to healthcare professionals.
In this article, we’ll explore how medical device packaging supports a resilient supply chain, adheres to regulatory standards, and enables medical device companies to maintain quality, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
The Vital Role of Packaging
As a mainstay of supply chain management, packaging fulfills several critical functions beyond simply protecting a product.
The global medical device packaging market was valued at USD 29.78 billion in 2020 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% by 2028, driven by the increasing demand for advanced packaging solutions in healthcare. In spite of that, the packaging ensures the safe delivery of life-saving devices, maintains sterility and provides protection from environmental factors, physical damage, and contamination. These roles are essential for safeguarding patient safety, meeting regulatory standards, and ensuring the medical device supply chain runs efficiently.
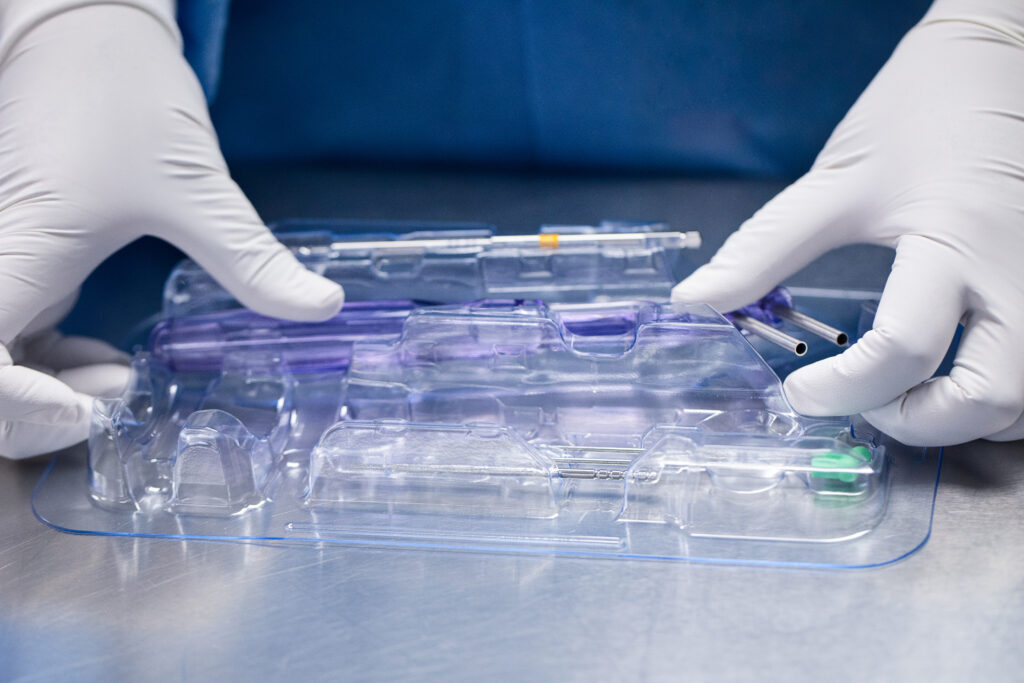
- Protecting Product Integrity and Patient Safety
Packaging ensures that medical products arrive at their destination intact and ready for use, safeguarding against damage during transit. Proper packaging shields devices from environmental factors like humidity, temperature fluctuations, and contamination. For sterile devices, the packaging must maintain sterility through the sterilization process and provide a barrier against microorganisms. This protection is crucial for preventing infections and ensuring patient safety, particularly in medical procedures that involve life-saving or high-risk interventions.
- Packaging Design for Usability and Accessibility
Packaging design directly impacts the day-to-day usability of medical devices for healthcare providers and patients. Beyond ensuring sterility and safety, packaging must be user-friendly, intuitive, and efficient. Features such as clear opening instructions, ergonomic designs for ease of handling, and visual indicators for proper use are particularly important in high-pressure medical environments. For example, tamper-evident seals and “clean peel” designs allow healthcare professionals to access sterile devices without compromising safety.
- Enabling Compliance with Regulatory Standards
ISO 11607 standards are the gold standard for medical device packaging, outlining requirements for design, materials, and validation processes. Adherence to these regulatory standards is non-negotiable, as non-compliant packaging can result in product recalls, regulatory penalties, or compromised patient outcomes. Packaging validation tests, such as sterility, burst, and barrier testing, ensure that materials and designs meet these stringent criteria. By showcasing compliance, manufacturers demonstrate their commitment to safety and regulatory excellence, strengthening trust with customers and stakeholders.
- Streamlining the Distribution Process
Efficient packaging in the supply chain simplifies logistics and accelerates the distribution process. Standardized packaging configurations allow for easy identification, stacking, and transport, ensuring that medical product supply chains operate smoothly. Proper labeling and tracking systems further enhance efficiency, reducing delays and transportation costs. For global markets, packaging must also comply with international regulations, ensuring that products reach healthcare providers without customs or legal complications.
- Global Supply Chain and Cross-Border Compliance
Packaging also plays an important role in ensuring seamless distribution across borders. Multilingual labeling and region-specific regulatory compliance are critical for avoiding delays in customs and ensuring product acceptance in diverse markets. For example, medical devices distributed in Europe must comply with CE marking requirements, while products entering North America face FDA labeling and material standards. Packaging must also account for varying climate conditions during transit, such as extreme heat, humidity, or cold, which can affect the integrity of both the packaging and the product.
- Reducing Potential Risks
Packaging plays a proactive role in mitigating risks associated with external factors such as natural disasters, supply chain disruptions, or mishandling during transit. Durable and adaptable packaging designs minimize the impact of these risks, ensuring that products remain safe, functional, and ready for use. For high-value or sensitive devices, packaging can include protective inserts, temperature controls, or tamper-evident seals, further safeguarding against damage or loss.
Packaging as a Cost-Saving Tool in the Supply Chain
It’s important to acknowledge that packaging isn’t just an expense—it’s an investment that can drive significant cost savings across the entire process. A McKinsey report highlights that efficient packaging strategies can reduce logistics costs by up to 30% and inventory carrying costs by 15% due to better spatial efficiency and real-time tracking.
- Optimizing Packaging Design for Efficiency:
Custom packaging solutions tailored to the dimensions and requirements of specific devices help minimize excess material usage while maximizing spatial efficiency. By reducing the size and weight of packaging, manufacturers can lower transportation costs and improve storage capacity. Additionally, streamlined designs facilitate easier handling for logistics providers and distribution teams, accelerating workflows and improving overall supply chain performance.
- Enabling Efficient Inventory Management:
Integrating features like barcodes, QR codes, or RFID tags into packaging designs simplifies inventory management and enables real-time product tracking. This technology provides critical visibility into stock levels, storage locations, and expiration dates, ensuring accurate deliveries to healthcare facilities. Effective inventory management helps avoid product waste, reduces the risk of stockouts, and supports better planning and allocation throughout the supply chain.
- Reducing Waste and Improving Handling:
Smartly designed packaging minimizes unnecessary material usage and simplifies handling processes. Configurations that optimize stacking and transport reduce the likelihood of damage or mismanagement during transit. This focus on efficient design lowers operational costs while maintaining product integrity, ensuring that medical devices arrive at their destination ready for use.
Collaboration Between Stakeholders
Effective packaging strategies in the medical device industry necessitate collaboration among various stakeholders, including manufacturers, packaging engineers, logistics providers, and healthcare professionals. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) emphasizes the importance of such collaborative communities, describing them as “continuing forums in which private- and public-sector members work together on medical device challenges to achieve common objectives and outcomes.”
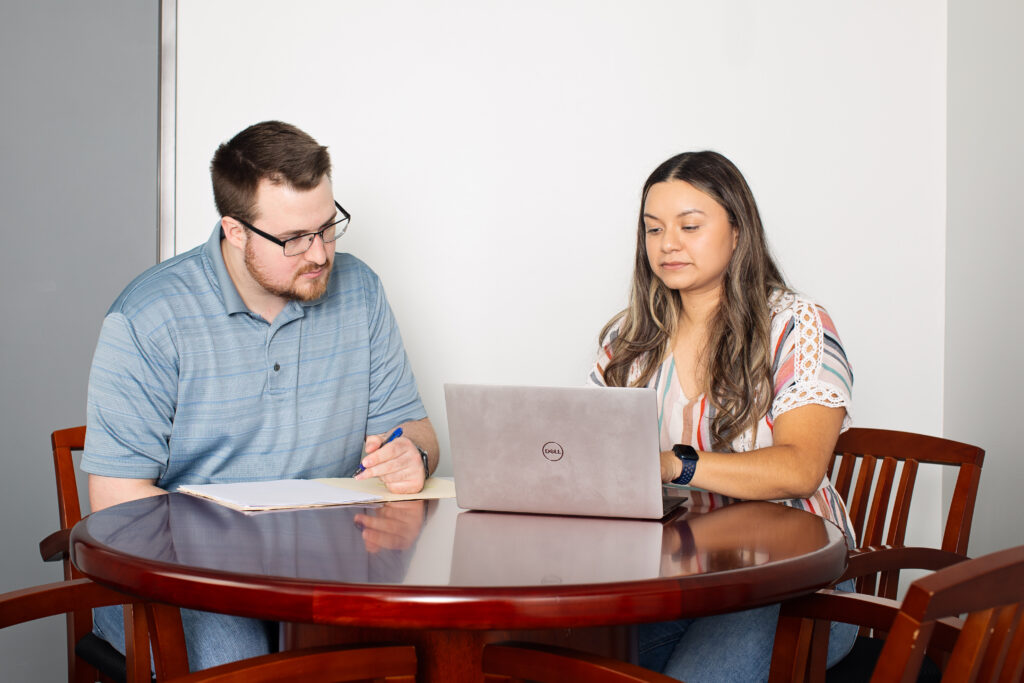

Cross-functional teams address challenges and develop innovative packaging solutions tailored to the medical device supply chain’s specific needs. For example, during the design phase, collaboration ensures that packaging configurations align with distribution requirements, thereby reducing inefficiencies. Engaging logistics providers early in the process streamlines transportation and storage, while input from healthcare professionals ensures that packaging meets end-user needs, such as intuitive opening and clear labeling. These collaborative efforts enhance the overall supply chain, reducing costs and improving outcomes for all stakeholders.
These collaborative efforts enhance the overall supply chain, reducing costs and improving outcomes for all stakeholders.
Packaging’s Role in Risk Mitigation and Supply Chain Resilience
In an increasingly unpredictable world, the medical device supply chain must be resilient to withstand external disruptions such as natural disasters, pandemics, and geopolitical conflicts. Packaging plays a critical role in fortifying this resilience. For medical device manufacturers, a proactive approach to risk mitigation through packaging is essential for maintaining patient safety, compliance, and operational efficiency.
- Preventing Physical Damage:
Packaging provides critical protection against physical impacts during handling, transportation, and storage. Shock-absorbent materials, reinforced structures, and tamper-evident seals shield medical products from damage that could compromise their functionality or sterility. For high-value devices or delicate surgical instruments, custom packaging solutions add an extra layer of security.
- Maintaining Product Integrity Under Environmental Stress:
Environmental conditions such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and exposure to light can jeopardize the quality of medical equipment. Packaging designed to withstand these environmental factors ensures that devices remain safe and effective, even during long-distance transport or storage in varying climates.
- Mitigating Compliance Risks:
Non-compliance with regulatory standards can lead to costly product recalls or damage to a company’s reputation. Packaging validation processes, such as sterility testing and durability assessments, help ensure that packaging meets strict ISO standards and industry regulations. By integrating compliance checks into the packaging processes, manufacturers can proactively address potential risks.
- Addressing Supply Chain Disruptions:
Unforeseen disruptions such as natural disasters or logistical delays can have a ripple effect across the medical supply chain. Resilient packaging minimizes the impact of such events, keeping products safe and functional until they reach their destination. Features like modular designs and standardized packaging sizes also enhance adaptability, allowing supply chains to recover quickly from interruptions.
- Reducing the Risk of Infection:
Improper packaging increases the risk of infection by allowing contaminants to compromise sterility. Features like medical device packaging validation, microbial barriers, and tamper-proof designs protect the integrity of sterile products, ensuring patient safety during critical medical procedures.
Conclusion: Elevating the Medical Device Supply Chain Through Packaging
From its role in safeguarding devices against environmental and physical challenges to its contribution to compliance and traceability, packaging remains a foundational element of supply chain success.
The potential for innovation within packaging design and processes is immense. As technologies like IoT sensors, blockchain systems, and automated validation become more integrated, packaging will play a pivotal role in shaping a supply chain that is not only efficient but also adaptable to future challenges. By prioritizing robust, versatile, and technology-driven packaging solutions, medical device manufacturers can reinforce their supply chain’s ability to meet the demands of an ever-evolving healthcare landscape.
Ultimately, packaging represents an opportunity for manufacturers to redefine standards, not just for safety and efficiency, but for reliability and innovation. Its strategic value lies in its capacity to support a resilient supply chain, one that ensures medical devices reach healthcare professionals and patients safely, effectively, and with a commitment to excellence.
FAQs
- Why is packaging critical in the medical device supply chain?
Packaging protects medical products from damage and contamination, ensures compliance with regulatory standards, and supports an efficient supply chain that delivers high-quality devices to healthcare providers.
- How does packaging impact patient safety?
Proper packaging maintains sterility, integrity, and functionality, preventing contamination and ensuring patient safety during critical medical procedures.
- How does technology enhance medical device packaging?
Smart packaging, RFID tracking, and automated validation processes improve transparency, risk mitigation, and efficiency, ensuring the delivery of high-quality devices under optimal conditions.
- What are the cost-saving benefits of optimized packaging design?
Efficient packaging configurations reduce material use, minimize transportation costs, and streamline inventory management, lowering operational expenses across the supply chain.
- How does packaging support supply chain resilience?
Durable, adaptable packaging designs protect devices from external factors like natural disasters and transit delays, ensuring a resilient supply chain capable of meeting customer demands.


